Female Infertility
Age
With the pass of the years, the function of the ovaries gradually decreases, affecting fertility from the age of 30, affecting ovulation quality at the age of 35 or more.
The younger you try to get pregnant, increase the chances of achieving it.
What is the ovarian reserve?
It is the woman capacity to be fertile. At birth, women are born with a certain number of eggs, as age increases, the ovarian reserve decreases, until menopause which is the end of a woman’s fertile life.
What are the main symptoms of low ovarian reserve?
It does not cause any symptoms, it can appear without the woman realize it. This is good reason to have periodic evaluations with the gynecologist, being ideal the evaluation by a sub-specialist in human reproduction.
Some people, may have menstrual alterations or vague symptoms such as headaches, hot flashes, tiredness, etc.
Weight
Overweight can directly affect ovular quality, increasing the risk of metabolic diseases such as insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus;
One of the main consequences of being overweight is affect the endometrium, which decreases the probability of embryo implantation, thus lowering pregnancy rates.
The probability of abortion is also increased in women who have a body mass index (BMI) higher than the ideal.
It is particularly important to maintain your ideal body mass index, avoiding underweight (BMI <20 kg/m2) or overweight (BMI >25kg/m2) that affect significantly reproduction. It is demonstrate, that loss of at least 5 to 10% of weight is associated with an improvement in the concentration of androgens.
Menstruation alterations
In a woman’s normal ovarian cycle, ovulation occurs every 14 days, meaning, the egg is released into the ovarian follicle through the fallopian tube where, fertilization occurs, if there is sperm to achieve pregnancy.
However, some women may present menstrual cycles alterations, like anovulation, which is the absence of an egg leaving the ovary, meaning that ovulation doesn’t happen, making it impossible for a spontaneous pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of anovulation?
Most of the time there’s absence of menstrual bleeding. It’s common for women who present anovulation not to have their period monthly. It means that they can be up to 6 months of periodless lapse.
Ovarian cysts
The ovaries generates woman’s eggs and are the ones to produce female hormones. Cysts are usually formed during ovulation (when the ovary releases an egg), and they’re usually harmless and disappear on their own.
Most women have them at some point in their lives.
How do I know if I have ovarian cysts? What symptoms may I have?
Most ovarian cysts are small and don’t cause symptoms. Women may not realize they have them until they have a pelvic exam. If you have symptoms, those may include:
- Pressure.
- Swelling.
- Inflammation.
- Lower abdomen pain, where the cyst may be located.
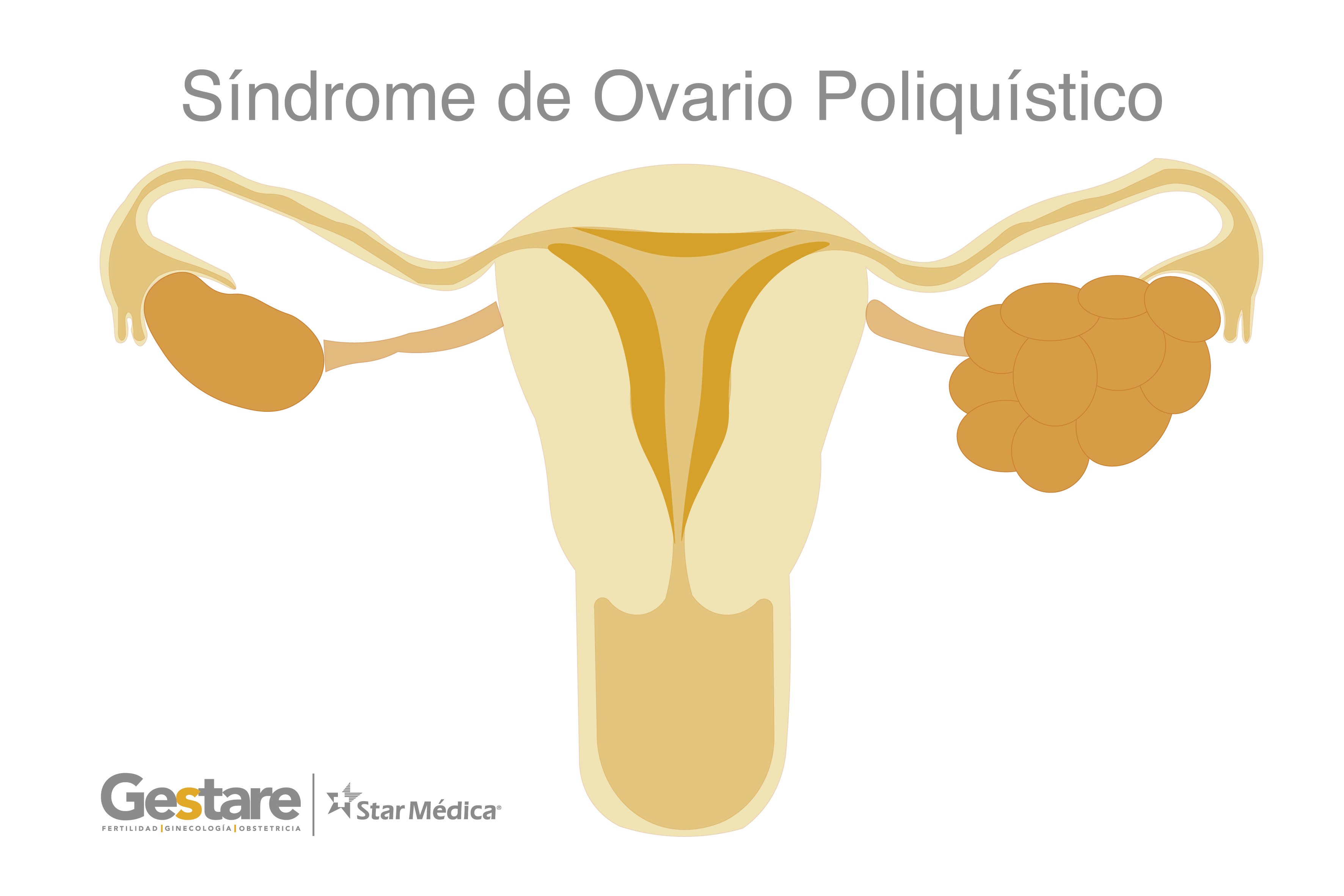
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the most common endocrine diseases in women at reproductive age. It’s characterized by:
- Infrequent or absent periods (every 2 or 3 months), therefore they have difficulties on getting pregnant.
- Infertility.
- Excess hair on the face, chest, abdomen, or thighs.
- Acne or oily skin and/or thick brown or black patches of skin.
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome are also at greater risk of developing diabetes, metabolic syndrome, heart disease and high blood pressure as it is more common in obese women.
If you have the one of the above symptoms and wish to get pregnant, a weight loss is suggested before starting any ovulation induction therapy. A loss of at least 5 to 10% of weight is associated with an improvement of androgen concentration and as well as spontaneous ovulation.
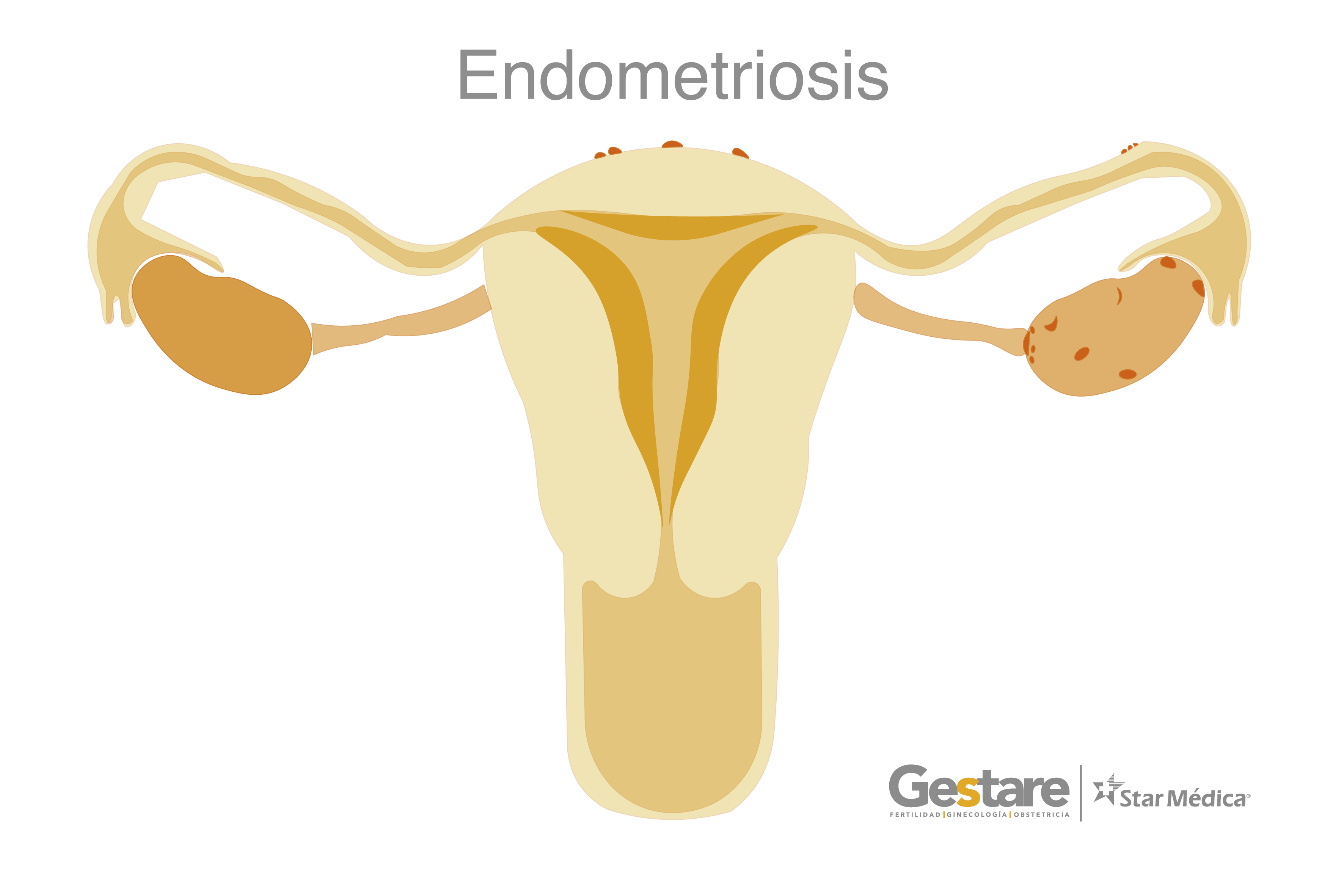
ENDOMETRIOSIS
Endometriosis is a disease characterized by the presence of endometrial glands and stromas in ectopic locations. That means that the tissue which is inside the uterus implants are placed outside the uterine cavity. Its clinical frame is very varied, which means that it may be difficult to the doctor to rule a diagnosis.
Among the main symptoms that may happen, are pain or abdominal cramps during the menstrual period which intensity can vary from intense to mild. Pain can happen when evacuating or urinating related to the period. Some women report intermittent headaches.
Endometriosis can be associated with infertility by damaging the pelvic organs and can create ovarian endometriomas that distort the adnexal anatomy and adhesions, causing tubal obstruction. Therapeutic behavior revolves around two fundamental axes: the symptomatology and the desire for pregnancy. It is important to individualize each case in order to give the best treatment, whether medical and/or surgical, if necessary.